Road Map¶
Book and AutomateTutorial
Basic and Environment
CSV
JSON
Project : Fetching Current Weather Data
Exercise
AutomateTutorial¶
- Work with Excel files in Python
- Work with CSV files and JSON in Python
- Task Schedule
- Sending Email
- Control Mouse & Keyboard
Basic and Environment¶
Check Modules Exist¶
You don't need to install csv 、 json 、 datetime and pprint, because they are in standard library.
Check Without Error Message!!
import csv
import json
import datetime
import pprint
import requests
Let's Start!¶
CSV (Comma-separated values)¶
CSV (Comma-separated values)¶
Everything is a string!¶
- Don’t have types for their values
- Don’t have settings for font size or color
- Don’t have multiple worksheets
- Can’t specify cell widths and heights
- Can’t have merged cells
- Can’t have images or charts embedded in them
Why csv?¶
- Easy and Clear
- Can open with Excel
Move the .csv file to the folder of Jupyter notebook¶
Where is my Jupyter notebook folder? Use 'os.getcwd()' to check!
In [1]:
import os
os.getcwd()
Out[1]:
'/home/amberfu/learn_CS/pythonAuto/PyLadies_Automate_JSON_CSV'
In [1]:
import csv
exampleFile = open('D2_01.csv')
exampleReader = csv.reader(exampleFile)
exampleReader
Out[1]:
<_csv.reader at 0x7fd38c13a7b8>
In [2]:
exampleData = list(exampleReader)
exampleData
Out[2]:
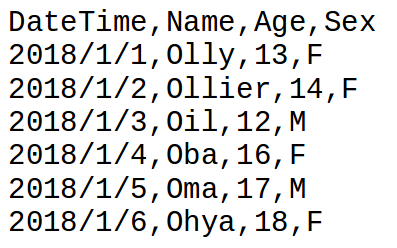
[['DateTime', 'Name', 'Age', 'Sex'], ['2018/1/1', 'Olly', '13', 'F'], ['2018/1/2', 'Ollier', '14', 'F'], ['2018/1/3', 'Oil', '12', 'M'], ['2018/1/4', 'Oba', '16', 'F'], ['2018/1/5', 'Oma', '17', 'M'], ['2018/1/6', 'Ohya', '18', 'F']]
In [3]:
exampleData[0][1]
Out[3]:
'Name'
In [4]:
exampleData[1][1]
Out[4]:
'Olly'
In [5]:
exampleData[1][0]
Out[5]:
'2018/1/1'
Reading Data from Reader Objects in a for Loop¶
In [6]:
import csv
exampleFile = open('D2_01.csv')
exampleReader = csv.reader(exampleFile)
for row in exampleReader:
print(row)
['DateTime', 'Name', 'Age', 'Sex'] ['2018/1/1', 'Olly', '13', 'F'] ['2018/1/2', 'Ollier', '14', 'F'] ['2018/1/3', 'Oil', '12', 'M'] ['2018/1/4', 'Oba', '16', 'F'] ['2018/1/5', 'Oma', '17', 'M'] ['2018/1/6', 'Ohya', '18', 'F']
In [7]:
import csv
exampleFile = open('D2_01.csv')
exampleReader = csv.reader(exampleFile)
for row in exampleReader:
print('Row #' + str(exampleReader.line_num) + ' ' + str(row))
Row #1 ['DateTime', 'Name', 'Age', 'Sex'] Row #2 ['2018/1/1', 'Olly', '13', 'F'] Row #3 ['2018/1/2', 'Ollier', '14', 'F'] Row #4 ['2018/1/3', 'Oil', '12', 'M'] Row #5 ['2018/1/4', 'Oba', '16', 'F'] Row #6 ['2018/1/5', 'Oma', '17', 'M'] Row #7 ['2018/1/6', 'Ohya', '18', 'F']
一次寫一筆資料:¶
csv_writer.writerow(list)
In [8]:
# 一次寫一筆資料:
import csv
outputFile = open('D2_02.csv', 'w', newline='') # open a new file to write!
outputWriter = csv.writer(outputFile)
outputWriter.writerow(['dog', 'cat', 'bird'])
outputWriter.writerow(['Hi, dog!', 'cat', 'bird'])
outputWriter.writerow([1, 2, 3.14])
outputFile.close()
Automatically escapes the comma with csv module:¶

一次寫多筆資料:¶
csv_writer.writerows(lists)
In [9]:
# 先看一下資料:
exampleData
Out[9]:
[['DateTime', 'Name', 'Age', 'Sex'], ['2018/1/1', 'Olly', '13', 'F'], ['2018/1/2', 'Ollier', '14', 'F'], ['2018/1/3', 'Oil', '12', 'M'], ['2018/1/4', 'Oba', '16', 'F'], ['2018/1/5', 'Oma', '17', 'M'], ['2018/1/6', 'Ohya', '18', 'F']]
In [10]:
import csv
outputFile = open('D2_02_rows.csv', 'w', newline='')
outputWriter = csv.writer(outputFile)
outputWriter.writerows(exampleData)
outputFile.close()
Notice!¶
If you forget to set the newline argument on Windows system...
Your row will be double-spaced!!!
In [11]:
import csv
outputFile = open('D2_03.csv', 'w') # <-- forget to set the newline argument! (In Windows system)
outputWriter = csv.writer(outputFile)
outputWriter.writerow(['dog', 'cat', 'bird'])
outputWriter.writerow(['Hi, dog!', 'cat', 'bird'])
outputWriter.writerow([1, 2, 3.14])
outputFile.close()
In [12]:
import csv
outputFile = open('D2_04.tsv', 'w', newline='') # tsv is mean tab-separated values
outputWriter = csv.writer(outputFile, delimiter='\t') # <-- default is comma
outputWriter.writerow(['dog', 'cat', 'bird'])
outputWriter.writerow(['Hi, dog!', 'cat', 'bird'])
outputWriter.writerow([1, 2, 3.14])
outputFile.close() # You can open tsv file with any text editor

JSON (JavaScript Object Notation)¶
JSON (JavaScript Object Notation)¶
- A popular way to format data as a single human-readable string
- Many websites make their data available in JSON format, and offer APIs (Application Programming Interfaces ) for programs to use
In [13]:
JasonString1 = '{"name": "Olly", "Female": true, "Height": 154, "Weight": null}'
type(JasonString1)
Out[13]:
str
In [14]:
import json
JasonAsPyValue =json.loads(JasonString1)
JasonAsPyValue
Out[14]:
{'Female': True, 'Height': 154, 'Weight': None, 'name': 'Olly'}
In [15]:
type(JasonAsPyValue)
Out[15]:
dict
In [16]:
JasonAsPyValue['Height']
Out[16]:
154
In [17]:
PyDict = {'Female': False, 'Height': None, 'Weight': 50, 'name': 'Ohbo'} # python's dict
type(PyDict)
Out[17]:
dict
In [18]:
import json
PyDictAsJason = json.dumps(PyDict)
PyDictAsJason
Out[18]:
'{"Female": false, "Height": null, "Weight": 50, "name": "Ohbo"}'
In [19]:
type(PyDictAsJason)
Out[19]:
str
Project : Fetching Current Weather Data¶
Enter OpenWeatherMap hit Sign Up¶
Create personal account¶
Find your personal API key after login¶
There is the document for Howt to Start¶

How to get the weather of Taipei?¶
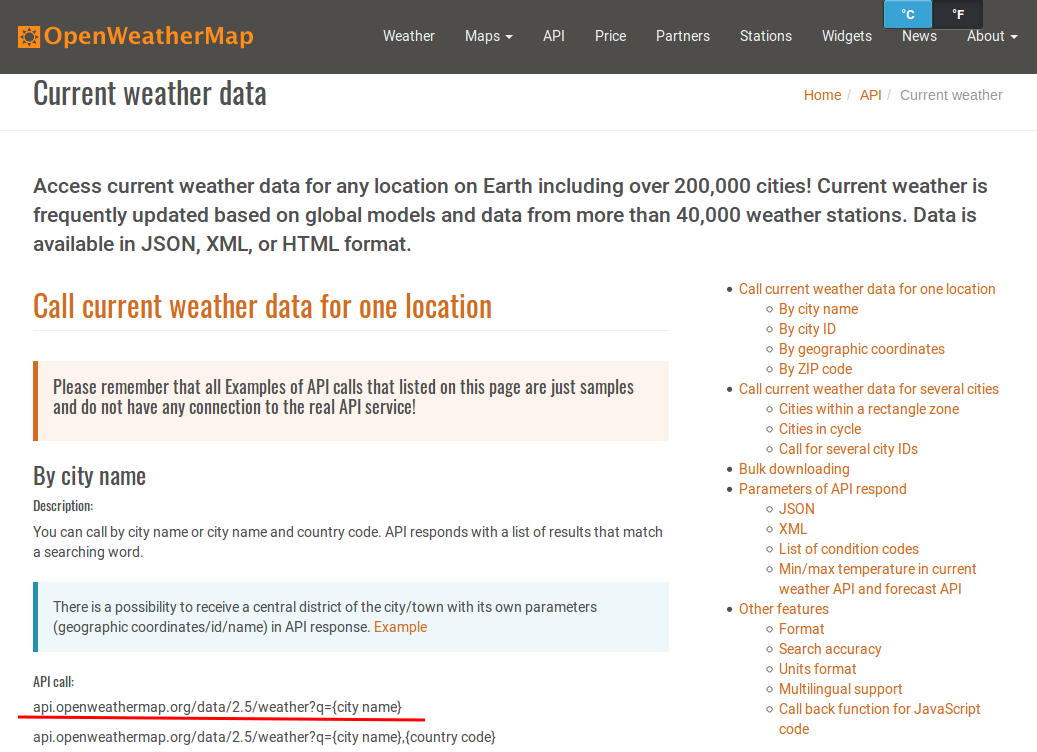
Step 1: Download the JSON Data¶
In [20]:
import json, requests
# 依照 API 說明放入: q=想查詢的城市名、 剛剛申請的 API Key
location = 'Taipei'
APPID = '2a2XXXdf24XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX'
url = 'http://api.openweathermap.org/data/2.5/weather?q=%s&APPID=%s'%(location, APPID)
# 使用 requests package 取得 json 資料:
response = requests.get(url)
response.raise_for_status() # 如果發送了一個錯誤請求,可以通過 Response.raise_for_status() 來抛出異常
In [21]:
response.text
Out[21]:
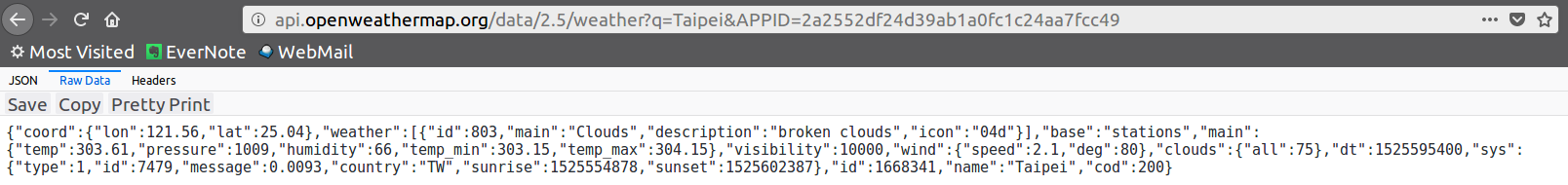
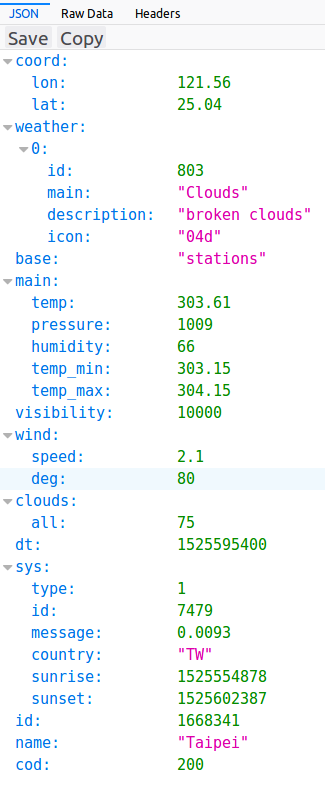
'{"coord":{"lon":121.56,"lat":25.04},"weather":[{"id":801,"main":"Clouds","description":"few clouds","icon":"02n"}],"base":"stations","main":{"temp":302.61,"pressure":1007,"humidity":70,"temp_min":302.15,"temp_max":303.15},"visibility":10000,"wind":{"speed":2.1,"deg":120},"clouds":{"all":20},"dt":1527420600,"sys":{"type":1,"id":7479,"message":0.0054,"country":"TW","sunrise":1527368692,"sunset":1527417432},"id":1668341,"name":"Taipei","cod":200}'
[補充] 快速上手 requests
In [22]:
# 用 json.loads() 讀取 API 資料:
weatherData = json.loads(response.text)
In [23]:
# 查看資料有哪些欄位(key值)
weatherData.keys()
Out[23]:
dict_keys(['coord', 'weather', 'base', 'main', 'visibility', 'wind', 'clouds', 'dt', 'sys', 'id', 'name', 'cod'])
In [24]:
weatherData
Out[24]:
{'base': 'stations',
'clouds': {'all': 20},
'cod': 200,
'coord': {'lat': 25.04, 'lon': 121.56},
'dt': 1527420600,
'id': 1668341,
'main': {'humidity': 70,
'pressure': 1007,
'temp': 302.61,
'temp_max': 303.15,
'temp_min': 302.15},
'name': 'Taipei',
'sys': {'country': 'TW',
'id': 7479,
'message': 0.0054,
'sunrise': 1527368692,
'sunset': 1527417432,
'type': 1},
'visibility': 10000,
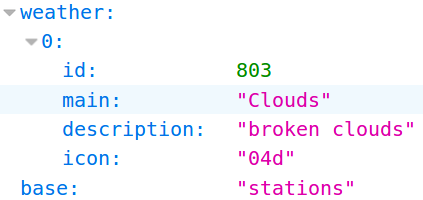
'weather': [{'description': 'few clouds',
'icon': '02n',
'id': 801,
'main': 'Clouds'}],
'wind': {'deg': 120, 'speed': 2.1}}
b. 直接下載範例資料¶
下載資料 D2_json.txt (已預先載好的 openweathermap)
Move the file to the folder of Jupyter notebook¶
Use os.getcwd() to check!
In [25]:
import json
import csv
exampleJSONFile = open('D2_json.txt')
weatherData = json.loads(exampleJSONFile.read())
exampleJSONFile.close()
weatherData
Out[25]:
{'base': 'stations',
'clouds': {'all': 40},
'cod': 200,
'coord': {'lat': 25.04, 'lon': 121.56},
'dt': 1526785200,
'id': 1668341,
'main': {'humidity': 63,
'pressure': 1009,
'temp': 306.07,
'temp_max': 307.15,
'temp_min': 305.15},
'name': 'Taipei',
'sys': {'country': 'TW',
'id': 7479,
'message': 0.0125,
'sunrise': 1526764037,
'sunset': 1526812412,
'type': 1},
'visibility': 10000,
'weather': [{'description': 'scattered clouds',
'icon': '03d',
'id': 802,
'main': 'Clouds'}],
'wind': {'deg': 310, 'speed': 3.6}}
In [26]:
weatherData.keys()
Out[26]:
dict_keys(['coord', 'weather', 'base', 'main', 'visibility', 'wind', 'clouds', 'dt', 'sys', 'id', 'name', 'cod'])
Get information of 'City', 'Datetime' and 'Weather'¶
- name : City name
- dt : Time of data calculation, unix, UTC
- weather.main : Group of weather parameters (Rain, Snow, Extreme etc.)
- weather.description : Weather condition within the group
In [27]:
city = weatherData['name']
dt = weatherData['dt']
weather = weatherData['weather'][0]
In [28]:
import pprint
print('city = ', city)
print('dt = ', dt)
print('weather = ', weather)
print('\npp.pprint :')
pp = pprint.PrettyPrinter(indent=4)
pp.pprint((city, dt, weather))
city = Taipei
dt = 1526785200
weather = {'id': 802, 'main': 'Clouds', 'description': 'scattered clouds', 'icon': '03d'}
pp.pprint :
( 'Taipei',
1526785200,
{ 'description': 'scattered clouds',
'icon': '03d',
'id': 802,
'main': 'Clouds'})
In [29]:
import datetime
dtime = datetime.datetime.fromtimestamp(dt).strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')
dtime
Out[29]:
'2018-05-20 11:00:00'
In [30]:
weatherData['weather']
Out[30]:
[{'description': 'scattered clouds',
'icon': '03d',
'id': 802,
'main': 'Clouds'}]
In [31]:
weatherData['weather'][0]
Out[31]:
{'description': 'scattered clouds', 'icon': '03d', 'id': 802, 'main': 'Clouds'}
In [32]:
w_main = weather['main'] # equal to weatherData['weather'][0]['main']
w_desc = weather['description'] # equal to weatherData['weather'][0]['description']
In [33]:
print(w_main)
print(w_desc)
Clouds scattered clouds
Print current wheather information¶
In [34]:
print('~~ Current Wheather ~~')
print('★ Location :\t', city)
print('★ Date Time :\t', dtime)
print('★ Weather :\t', w_main, '-', w_desc)
~~ Current Wheather ~~ ★ Location : Taipei ★ Date Time : 2018-05-20 11:00:00 ★ Weather : Clouds - scattered clouds
Step 3 : Keep Weather Information as csv file¶
In [35]:
import csv, json
outputFile = open('D2_05.csv', 'w', newline='')
outputWriter = csv.writer(outputFile)
outputWriter.writerow([city, dtime, w_main, w_desc])
outputFile.close()
查看匯出的 csv 檔案:
Exercise¶
Work with CSV files & JSON in Python¶
寫一個 function ,包含下列功能:¶
- Import csv & json & requests
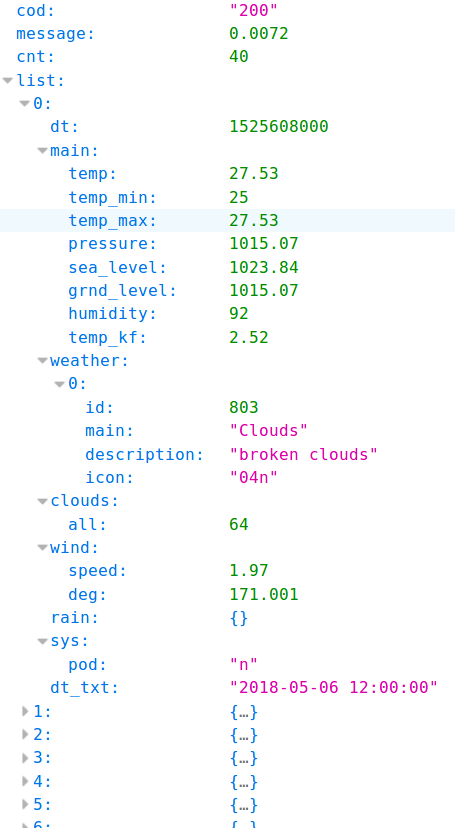
Get 5/3hrs days weahter forecast result for Taipei from OpenWeatherMap
API call:
http://api.openweathermap.org/data/2.5/forecast?q={city}&units=metric&APPID={APPID}Parameters:
- q : city name
- units=metric : Temperature (Celsius)
- APPID : API Key
- Write data as csv file
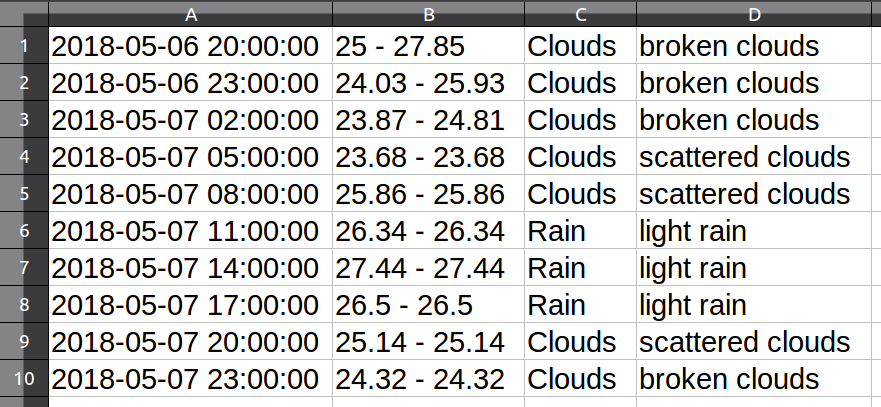
看一下需要處理的資料:¶
Answer¶
In [36]:
import csv, json, requests, datetime
def Forecast30hrs(location, csvfile_path, APPID):
# Use openweathermap API get json sting
url = 'http://api.openweathermap.org/data/2.5/forecast?q=%s&units=metric&APPID=%s' %(location, APPID)
response = requests.get(url)
response.raise_for_status()
# load json as dict()
weatherData = json.loads(response.text)
# Get weather information by the key of dict()
w = weatherData['list']
# Open csv file
outputFile = open(csvfile_path, 'w', newline='')
outputWriter = csv.writer(outputFile)
# Write column names
outputWriter.writerow(['Forecast datetime', 'Temp. Range (Celsius)', \
'Group of weather parameters', 'Weather condition within the group'])
for i in range(10):
# Get Forecast datetime, min/max daily temperature, main, description
dtime = datetime.datetime.fromtimestamp(w[i]['dt']).strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')
temp_min = w[i]['main']['temp_min']
temp_max = w[i]['main']['temp_max']
main = w[i]['weather'][0]['main']
desc = w[i]['weather'][0]['description']
# Write rows into csv file
outputWriter.writerow([dtime, str(temp_min)+ ' - ' +str(temp_max), main, desc])
outputFile.close()
Check your function:¶
In [37]:
location = 'Taipei'
csvfile_path = 'D2_Exercise.csv'
APPID = 'fit your API key..._' # <-- FIT your key here!
Forecast30hrs(location, csvfile_path, APPID)
Check output file:¶